Table of contents
Array
An Array is a sequential collection of elements. It is the most used data structure used by programmers. It can contain elements of multiple data types. Each element of an array can be referred using an index. In an array, the indices start with 0 (the first element has the index 0) , this demonstrates the distance between the current element and the first element. Click here to find out why indices of an array start with 0 and not 1. An array can have as many as 32 dimensions, although with each dimension memory requirements of an array increase considerably.
Following are some of the most used array methods in javascript.
Array Methods in Javascript:
- map():
map method is used to apply a function to all the elements of an array and store them in a new array without affecting the original array:

const mapped = arr.map(element => element + 10);

- filter():
filter method is used to use a function as a condition filter out all the elements of an array
which pass the condition and store them in a new array without affecting the original array:
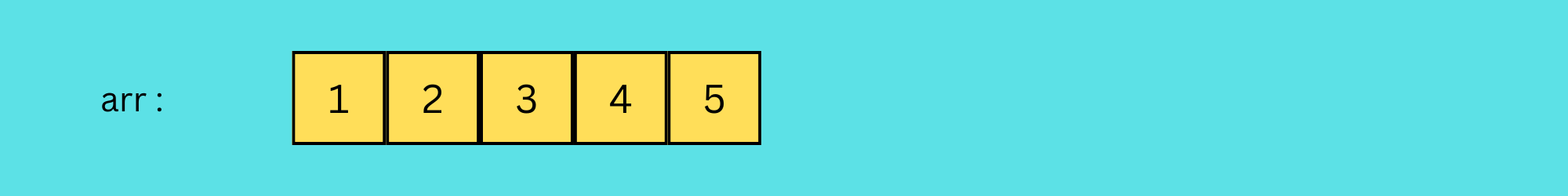
const filtered = arr.filter(element => element === 1 || element === 4);

- sort():
sort is used to sort elements of an array in ascending or descending order.


const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const arr2 = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1];
arr.sort((a, b) => a > b ? -1 : 1); // descending order
arr2.sort((a, b) => a > b ? 1 : -1); // ascending order


- forEach():
forEach loops over an array and executes a callback function on each of its elements.
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
arr.forEach(element => {
console.log(element);
});
// 1
// 2
// 3
// 4
// 5
- concat():
concat is used to merge multiple arrays and return a new array without affecting existing ones.

const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const arr2 = [6, 7, 8, 9, 10];
const merged = arr.concat(arr2);

- every():
every checks if each element of an array passes the given condition or not. Returns true only if every element passes the condition, else returns false.
const arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const greaterThan3 = arr.every(element => element > 3);
console.log(greaterThan3); // false
const lessThan6 = arr.every(element => element < 6);
console.log(lessThan6); // true
- some():
some checks if at least one element passes the given condition or not. Returns true is at least one element passes the condition, else returns false.
const arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const greaterThan3 = arr.some(element => element > 3);
console.log(greaterThan3); // true
const greaterThan6 = arr.every(element => element > 6);
console.log(lessThan6); // false
- includes():
includes checks is the array contains a certain element. Returns true if it is present, false otherwise.
const arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
console.log(arr.includes(2)) // true;
console.log(arr.includes(7)) // false;
- join():
join joins all the elements of an array and returns a new string.
const arr = [ "j", "a", "v", "a", "s", "c", "r", "i", "p", "t"];
console.log(arr.join(''));
- reduce():
reduce reduces an array to a single value and returns it. A "reducer" call-back function is applied to every element of an element to reduce it.
const arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
console.log(arr.reduce((total, current) => total + current)); // 15
- find():
find returns the first element of an array which passes a certain condition. Returns undefined if not found.
const arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
console.log(arr.find(element => element > 3)); // 4
- findIndex():
findIndex returns the index of the first element of an array which passes a certain condition. Returns -1 if not found.
const arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
console.log(arr.findIndex(element => element > 3)); // 3
- indexOf():
indexOf returns the index of the first occurrence of an element in an array. Returns -1 if not found.
const arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
console.log(arr.indexOf(2)); // 1
- fill():
fill fills the array with a static value.

const arr = new Array (5);
arr.fill(10);

- slice():
slice returns a new array with the elements present in the specified range.

const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const sliced = arr.slice(1, 3);

- reverse():
reverse reverses an array.

arr.reverse();

- push():
push adds elements to an array and returns it's length

const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
console.log(arr.push(6)); // 6

- pop():
pop removes the last element from an array and returns it.

console.log(arr.pop()); // 5

- shift():
shift removes the first element from the array and returns it.

console.log(arr.shift()); // 1

- unshift():
unshift adds elements to the start of an array and returns the new length

console.log(arr.unshift(0)); // 6

